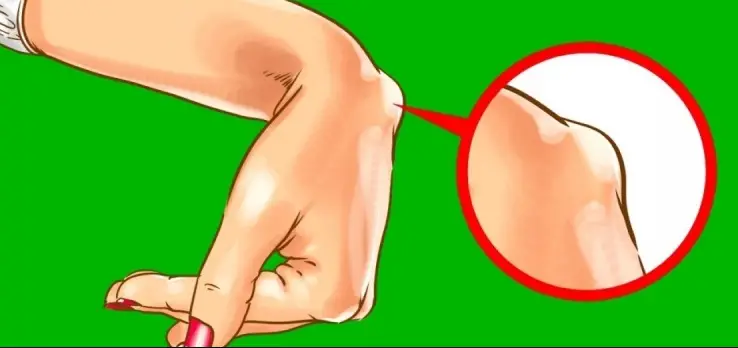
Wrist pain is a common health problem which can be caused by various reasons. Even though the wrist pain usually results from overuse of the hands or sudden injuries, in some cases, it can be a sign of some more serious condition. Wrist injuries can occur due to a broken bone, infection, inflammation, abnormal growths, cysts, and tumors. A swelling in the wrist can be caused by strains, sprains, bone fractures, tendinitis, bursitis, arthritis, as well as benign or malignant growth. Not every wrist injury is a sign of some serious problem. However, if you experience any pain and swelling in the wrists, you should immediately visit your doctor in order to get an accurate diagnosis and to receive a proper treatment. Here are the major health conditions that can cause wrist pain.
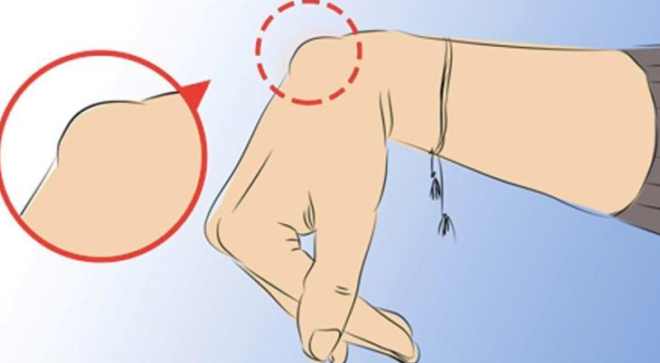
Credits to: www.womendailymagazine.com
Ganglion Cysts
Ganglion cysts are noncancerous lumps that develop mainly on the wrists. They are linked to degeneration of a synovial cyst or another connective tissue next to the joint, usually a tendon or ligament. The cause of ganglion cysts is unknown. Some theories suggest that they result from a past trauma. The cysts can grow up to 2.5 cm in size.
Lipomas
Lipomas are benign tumors that can develop in the wrist or on the palm. These tumors can be extremely debilitating and may make you unable to extend your fingers. When the lipomas compress the nerves, they are likely to cause excessive pain and sensitivity.
De Quervain Syndrome
De Quervain Syndrome is a condition characterized by an occurrence of pain, swelling, and soreness in the wrists, as well as a formation of cysts and nodules. This syndrome thickens the extensor ligament of the thumb up to twice its size, making any wrist movement very painful.
Tenosynovitis
Tenosynovitis is an inflammation and swelling of the fluid-filled sheath, or synovium, surrounding a tendon. This condition is caused by stress or microtrauma, and most commonly affects people who have physical jobs. The inflammation has an effect on the short extensor in the thumb and the abductor muscle, which can thicken the ligament and damage the sheath.