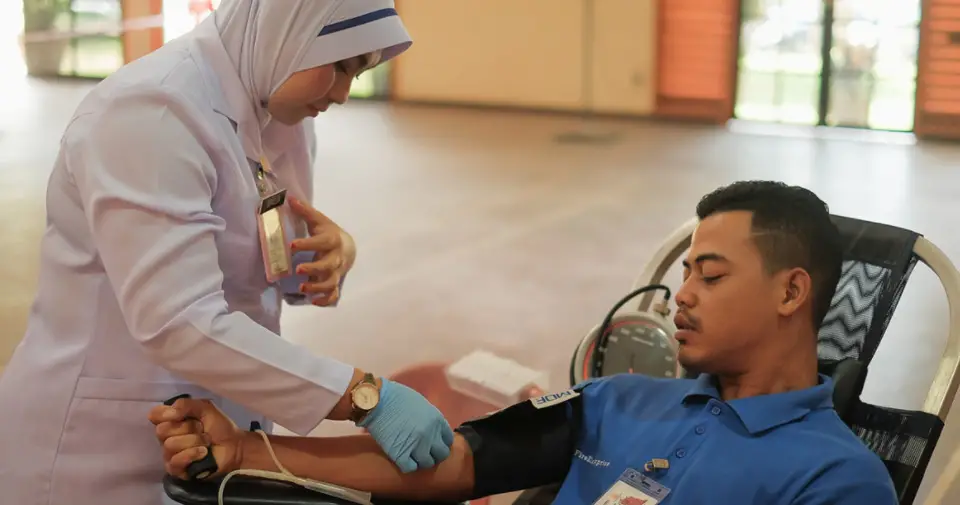
There is one gift that many people can give to one another that has the power to save lives. Blood donation is a voluntary act that can help save other people’s lives. There are several types of blood donation. The most common type is whole blood donation which is later broken down into its components: red blood cells, plasma and platelets. In this way one blood donation can save up to three lives. Another type of blood donation is apheresis, a procedure in which the donor is attached to a machine that can collect and separate individual blood components (red blood cells, plasma, or platelets) and return the unused components back to the donor.
How are blood components used?
Donor platelets are usually given to people with leukemia, people receiving chemotherapy, or people with severe infections. People with severe blood loss (for example, after an injury or accident), or people with severe anemia have a medical need for red blood cells, which deliver oxygen to all cells in the body. Plasma is usually given to people with liver damage, burns, and severe bacterial infections in the blood. Donor blood makes all this possible. There is no substitute for human blood.
Is blood donation safe?
Blood donation is safe. New, sterile disposable equipment is used for each donor, so there is no risk of infection. Any healthy adult, aged 18 to 65, can donate blood without compromising their own health. Within 24 hours after donating blood, the body will make up for the lost fluid, and after a few weeks the lost red blood cells will be made up. To be a blood donor, each person must pass an assessment of physical health and medical history.
Recommendations before donating blood
Get plenty of sleep the night before your planned blood donation. Keep your meal healthy before donating blood, and avoid fatty foods such as burgers, french fries, bacon or ice cream. Drink more water and other fluids than usual.
Health benefits for blood donors
According to a report by the British Mental Health Foundation, helping others by donating blood can: reduce stress, improve emotional well-being, improve physical health, help relieve negative feelings, provide a sense of belonging and reduce insulation. There are studies that provide evidence of a lower risk of heart disease in blood donors due to reduced blood viscosity and reduced iron stores.
Do not worry, the amount of blood in the body is not limited.
The average adult has about 5 liters of blood in the body. About 400 milliliters are taken during the donation, and the body will quickly make up for the blood you donated.
Who can donate blood?
For a person to become a blood donor, first of all, he must be a healthy person between 18 and 65 years old, and in specific cases both younger and older. Women can donate blood every four months, and men every three months.
Vegetarians can also donate blood
The survey found that 3 percent of 2,000 respondents believe that vegetarians can not donate blood. The main problem is the concern about iron in the blood and the concern that the vegetarian diet does not have much iron. If your blood iron level is lower than normal, you will be temporarily rejected as a blood donor – for your own safety. But if you eat a balanced diet, you probably have enough iron in your body.
Neither tattoos nor piercings prevent you from donating blood
It is true that if you have had a tattoo or piercing recently, you may be temporarily unable to donate blood. The rule is clear: it must take some time from tattooing or piercing to donating blood. The period varies across countries.
If you have been ill, you will have to wait until the next blood donation
If you want to donate blood and have been ill or on therapy before, you will have to wait a while. The time of prohibition depends on the disease. Thus, seven days should elapse between the onset of the common cold and the transfusion. When it comes to medication, seven days is the time it takes to take antibiotics and donate blood.
Sex rules are less complicated than you think
You can donate blood without delay unless you have been in a relationship with an HIV-positive person or a person with hepatitis B or hepatitis C for the last 180 days. Reasons for a permanent ban on blood donation include high-risk sexual behavior, chronic alcoholism, and drug addiction. Even people who have HIV, hepatitis B and C, syphilis, tropical diseases can not donate blood.